The acoustic guitar is a versatile and popular instrument with a rich history and a distinctive sound that has influenced many music genres. Whether you’re a budding musician or simply curious about the instrument, understanding the basics of acoustic guitar can set you on the right path.
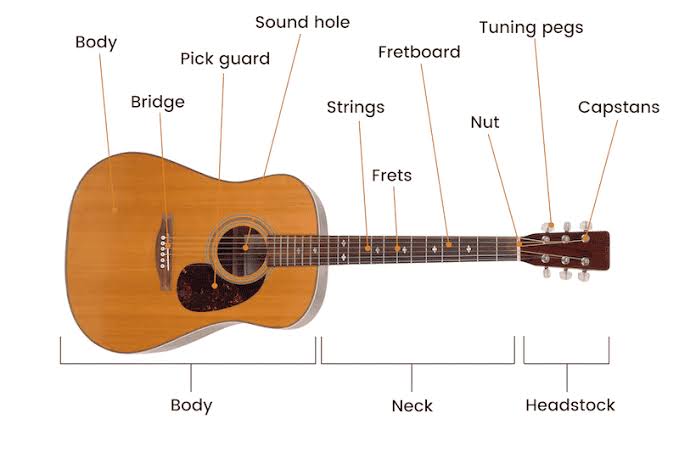
Anatomy of an Acoustic Guitar
- Body: The main part of the guitar, usually made of wood. It includes:
– Top (Soundboard): Often made from spruce or cedar, it affects the tone and volume. – Back and Sides: Typically made from mahogany, rosewood, or maple, contributing to the guitar’s resonance and tone.
- Neck: The long, thin part extending from the body, usually made of mahogany or maple.
– Fretboard (Fingerboard): Attached to the neck, where you press the strings to create different notes. Commonly made from rosewood or ebony.
- Headstock: The top part of the guitar, containing the tuning pegs (machine heads) that adjust the tension of the strings.
- Bridge: Located on the body, it holds the strings in place and transfers their vibrations to the soundboard.
- Soundhole: The opening in the body that helps project the sound.
- Strings: Typically made of steel or nylon, they vibrate to produce sound. Most acoustic guitars have six strings.

Choosing an Acoustic Guitar
When selecting an acoustic guitar, consider the following factors:
- Body Shape and Size: Different shapes (dreadnought, concert, jumbo, etc.) offer varied tones and playability.
- Tonewoods: The type of wood used can significantly impact the sound. Experiment with different woods to find your preferred tone.
- Playability: Ensure the guitar is comfortable to hold and play. Check the neck width, string action, and overall feel.
- Budget: There are quality guitars available at various price points. Determine your budget and seek the best value within it.
Basic Techniques
- Tuning: Standard tuning for an acoustic guitar is E-A-D-G-B-e (from lowest to highest string). Use a tuner to ensure accurate pitch.
- Strumming: Practice using a pick or your fingers to strum across the strings rhythmically.
- Fingerpicking: Use your fingers to pluck individual strings, creating intricate patterns.
- Chords: Learn basic chords (A, E, D, G, C) and practice transitioning between them smoothly.
- Scales: Familiarize yourself with major and minor scales to improve finger dexterity and understand musical structure.

Maintenance Tips
- Cleaning: Wipe down the strings and body after playing to remove oils and dirt.
- String Replacement: Change strings regularly to maintain sound quality. The frequency depends on usage, but typically every 1-3 months.
- Humidity Control: Keep your guitar in a stable environment to prevent wood from warping. Use a humidifier if necessary.
- Storage: Store your guitar in a case when not in use to protect it from damage.

Learning Resources
- Online Tutorials: Platforms like YouTube and dedicated guitar lesson websites offer tutorials for all skill levels.
- Books: Instructional books can provide structured learning.
- Classes: Consider taking lessons from a professional instructor for personalized guidance.
- Practice: Consistent practice is crucial for improvement. Set aside regular time each day to practice.
Conclusion
The acoustic guitar is a rewarding instrument that offers endless possibilities for musical expression. By understanding its anatomy, choosing the right guitar, mastering basic techniques, and maintaining your instrument, you’ll be well on your way to becoming a proficient guitarist. Happy playing!

